Total, Direct, and Indirect Effects of X on Y Through M Over a Specific Time Interval or a Range of Time Intervals
Source:R/cTMed-med.R
Med.RdThis function computes the total, direct, and indirect effects of the independent variable \(X\) on the dependent variable \(Y\) through mediator variables \(\mathbf{m}\) over a specific time interval \(\Delta t\) or a range of time intervals using the first-order stochastic differential equation model's drift matrix \(\boldsymbol{\Phi}\).
Arguments
- phi
Numeric matrix. The drift matrix (\(\boldsymbol{\Phi}\)).
phishould have row and column names pertaining to the variables in the system.- delta_t
Vector of positive numbers. Time interval (\(\Delta t\)).
- from
Character string. Name of the independent variable \(X\) in
phi.- to
Character string. Name of the dependent variable \(Y\) in
phi.- med
Character vector. Name/s of the mediator variable/s in
phi.- tol
Numeric. Smallest possible time interval to allow.
Value
Returns an object
of class ctmedmed which is a list with the following elements:
- call
Function call.
- args
Function arguments.
- fun
Function used ("Med").
- output
A matrix of total, direct, and indirect effects.
Details
See Total(),
Direct(), and
Indirect() for more details.
Linear Stochastic Differential Equation Model
The measurement model is given by $$ \mathbf{y}_{i, t} = \boldsymbol{\nu} + \boldsymbol{\Lambda} \boldsymbol{\eta}_{i, t} + \boldsymbol{\varepsilon}_{i, t}, \quad \mathrm{with} \quad \boldsymbol{\varepsilon}_{i, t} \sim \mathcal{N} \left( \mathbf{0}, \boldsymbol{\Theta} \right) $$ where \(\mathbf{y}_{i, t}\), \(\boldsymbol{\eta}_{i, t}\), and \(\boldsymbol{\varepsilon}_{i, t}\) are random variables and \(\boldsymbol{\nu}\), \(\boldsymbol{\Lambda}\), and \(\boldsymbol{\Theta}\) are model parameters. \(\mathbf{y}_{i, t}\) represents a vector of observed random variables, \(\boldsymbol{\eta}_{i, t}\) a vector of latent random variables, and \(\boldsymbol{\varepsilon}_{i, t}\) a vector of random measurement errors, at time \(t\) and individual \(i\). \(\boldsymbol{\nu}\) denotes a vector of intercepts, \(\boldsymbol{\Lambda}\) a matrix of factor loadings, and \(\boldsymbol{\Theta}\) the covariance matrix of \(\boldsymbol{\varepsilon}\).
An alternative representation of the measurement error is given by $$ \boldsymbol{\varepsilon}_{i, t} = \boldsymbol{\Theta}^{\frac{1}{2}} \mathbf{z}_{i, t}, \quad \mathrm{with} \quad \mathbf{z}_{i, t} \sim \mathcal{N} \left( \mathbf{0}, \mathbf{I} \right) $$ where \(\mathbf{z}_{i, t}\) is a vector of independent standard normal random variables and \( \left( \boldsymbol{\Theta}^{\frac{1}{2}} \right) \left( \boldsymbol{\Theta}^{\frac{1}{2}} \right)^{\prime} = \boldsymbol{\Theta} . \)
The dynamic structure is given by $$ \mathrm{d} \boldsymbol{\eta}_{i, t} = \left( \boldsymbol{\iota} + \boldsymbol{\Phi} \boldsymbol{\eta}_{i, t} \right) \mathrm{d}t + \boldsymbol{\Sigma}^{\frac{1}{2}} \mathrm{d} \mathbf{W}_{i, t} $$ where \(\boldsymbol{\iota}\) is a term which is unobserved and constant over time, \(\boldsymbol{\Phi}\) is the drift matrix which represents the rate of change of the solution in the absence of any random fluctuations, \(\boldsymbol{\Sigma}\) is the matrix of volatility or randomness in the process, and \(\mathrm{d}\boldsymbol{W}\) is a Wiener process or Brownian motion, which represents random fluctuations.
References
Bollen, K. A. (1987). Total, direct, and indirect effects in structural equation models. Sociological Methodology, 17, 37. doi:10.2307/271028
Deboeck, P. R., & Preacher, K. J. (2015). No need to be discrete: A method for continuous time mediation analysis. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 23 (1), 61-75. doi:10.1080/10705511.2014.973960
Pesigan, I. J. A., Russell, M. A., & Chow, S.-M. (2025). Inferences and effect sizes for direct, indirect, and total effects in continuous-time mediation models. Psychological Methods. doi:10.1037/met0000779
Ryan, O., & Hamaker, E. L. (2021). Time to intervene: A continuous-time approach to network analysis and centrality. Psychometrika, 87 (1), 214-252. doi:10.1007/s11336-021-09767-0
See also
Other Continuous-Time Mediation Functions:
BootBeta(),
BootBetaStd(),
BootIndirectCentral(),
BootMed(),
BootMedStd(),
BootTotalCentral(),
DeltaBeta(),
DeltaBetaStd(),
DeltaIndirectCentral(),
DeltaMed(),
DeltaMedStd(),
DeltaTotalCentral(),
Direct(),
DirectStd(),
Indirect(),
IndirectCentral(),
IndirectStd(),
MCBeta(),
MCBetaStd(),
MCIndirectCentral(),
MCMed(),
MCMedStd(),
MCPhi(),
MCPhiSigma(),
MCTotalCentral(),
MedStd(),
PosteriorBeta(),
PosteriorIndirectCentral(),
PosteriorMed(),
PosteriorTotalCentral(),
Total(),
TotalCentral(),
TotalStd(),
Trajectory()
Examples
phi <- matrix(
data = c(
-0.357, 0.771, -0.450,
0.0, -0.511, 0.729,
0, 0, -0.693
),
nrow = 3
)
colnames(phi) <- rownames(phi) <- c("x", "m", "y")
# Specific time interval ----------------------------------------------------
Med(
phi = phi,
delta_t = 1,
from = "x",
to = "y",
med = "m"
)
#> Call:
#> Med(phi = phi, delta_t = 1, from = "x", to = "y", med = "m")
#>
#> Total, Direct, and Indirect Effects
#>
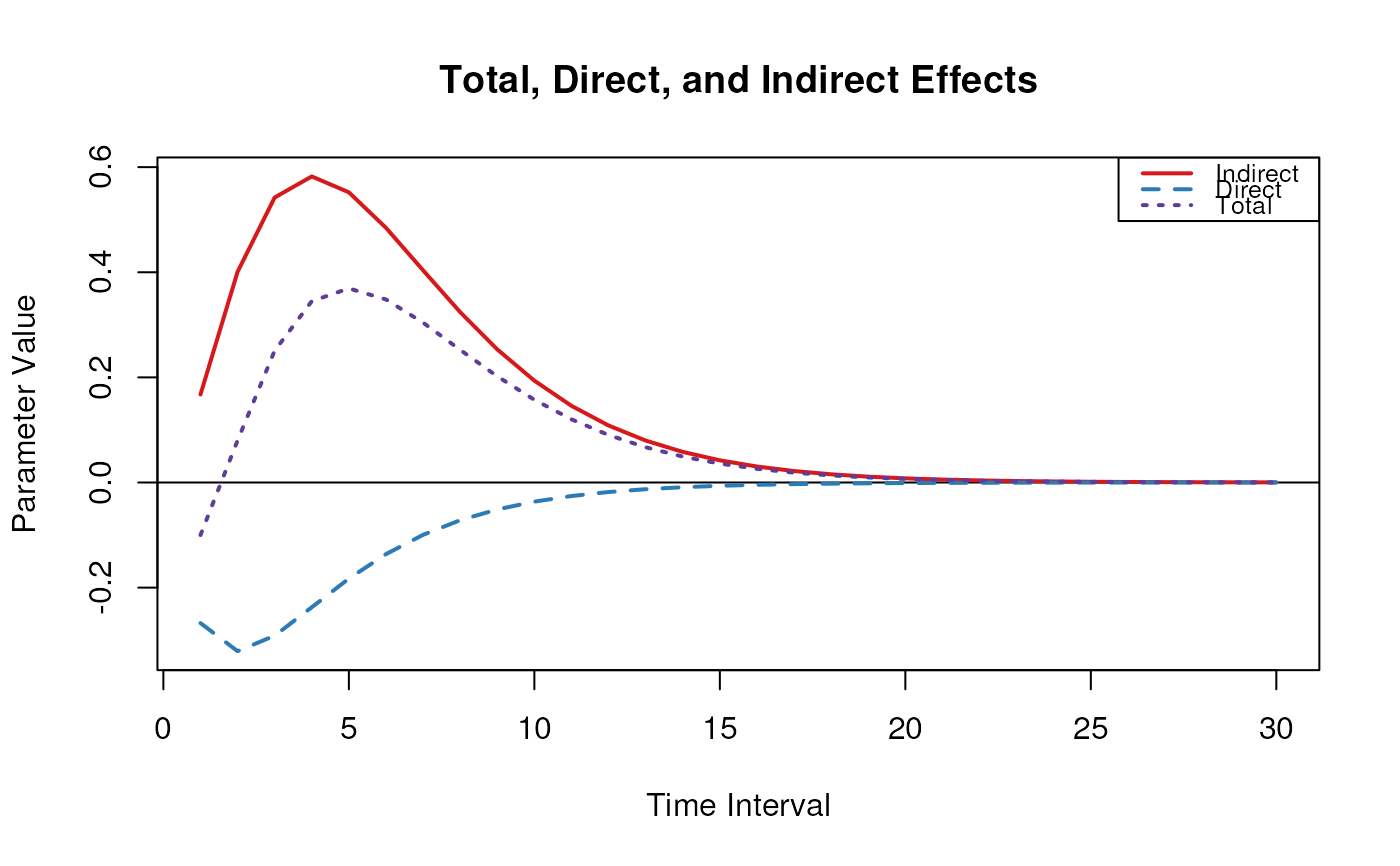
#> interval total direct indirect
#> [1,] 1 -0.1 -0.2675 0.1674
# Range of time intervals ---------------------------------------------------
med <- Med(
phi = phi,
delta_t = 1:30,
from = "x",
to = "y",
med = "m"
)
plot(med)
 # Methods -------------------------------------------------------------------
# Med has a number of methods including
# print, summary, and plot
med <- Med(
phi = phi,
delta_t = 1:5,
from = "x",
to = "y",
med = "m"
)
print(med)
#> Call:
#> Med(phi = phi, delta_t = 1:5, from = "x", to = "y", med = "m")
#>
#> Total, Direct, and Indirect Effects
#>
#> interval total direct indirect
#> [1,] 1 -0.1000 -0.2675 0.1674
#> [2,] 2 0.0799 -0.3209 0.4008
#> [3,] 3 0.2508 -0.2914 0.5423
#> [4,] 4 0.3449 -0.2374 0.5823
#> [5,] 5 0.3693 -0.1828 0.5521
summary(med)
#> Call:
#> Med(phi = phi, delta_t = 1:5, from = "x", to = "y", med = "m")
#>
#> Total, Direct, and Indirect Effects
#>
#> interval total direct indirect
#> [1,] 1 -0.1000 -0.2675 0.1674
#> [2,] 2 0.0799 -0.3209 0.4008
#> [3,] 3 0.2508 -0.2914 0.5423
#> [4,] 4 0.3449 -0.2374 0.5823
#> [5,] 5 0.3693 -0.1828 0.5521
plot(med)
# Methods -------------------------------------------------------------------
# Med has a number of methods including
# print, summary, and plot
med <- Med(
phi = phi,
delta_t = 1:5,
from = "x",
to = "y",
med = "m"
)
print(med)
#> Call:
#> Med(phi = phi, delta_t = 1:5, from = "x", to = "y", med = "m")
#>
#> Total, Direct, and Indirect Effects
#>
#> interval total direct indirect
#> [1,] 1 -0.1000 -0.2675 0.1674
#> [2,] 2 0.0799 -0.3209 0.4008
#> [3,] 3 0.2508 -0.2914 0.5423
#> [4,] 4 0.3449 -0.2374 0.5823
#> [5,] 5 0.3693 -0.1828 0.5521
summary(med)
#> Call:
#> Med(phi = phi, delta_t = 1:5, from = "x", to = "y", med = "m")
#>
#> Total, Direct, and Indirect Effects
#>
#> interval total direct indirect
#> [1,] 1 -0.1000 -0.2675 0.1674
#> [2,] 2 0.0799 -0.3209 0.4008
#> [3,] 3 0.2508 -0.2914 0.5423
#> [4,] 4 0.3449 -0.2374 0.5823
#> [5,] 5 0.3693 -0.1828 0.5521
plot(med)
