Benchmark: Comparing the Monte Carlo Method with Nonparametric Bootstrapping
Ivan Jacob Agaloos Pesigan
2025-10-19
Source:vignettes/benchmark.Rmd
benchmark.RmdWe compare the Monte Carlo (MC) method with nonparametric bootstrapping (NB) for standardized regression coefficients. In this example, we use the data set and the model used in betaMC: Example Using the BetaMC Function.
library(betaMC)
library(boot)
library(microbenchmark)The BetaMC() function is used to generate MC confidence
intervals. The BetaNB() function is used to generate NB
confidence intervals.
BetaNB <- function(formula, data, B) {
statistic <- function(formula, data, indices) {
return(
coef(lm(formula = formula, data = as.data.frame(scale(data[indices, ]))))[-1]
)
}
return(boot.ci(boot(data = data, statistic = statistic, formula = formula, R = B)))
}Data and Model
df <- betaMC::nas1982Benchmark
Arguments
| Variables | Values | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| R | 5000 | Number of Monte Carlo replications. |
| B | 5000 | Number of bootstrap samples. |
benchmark <- microbenchmark(
MC = {
formula <- "QUALITY ~ NARTIC + PCTGRT + PCTSUPP"
object <- lm(formula = formula, data = df)
mc <- MC(object = object, R = R, type = "mvn")
BetaMC(object = mc)
},
NB = {
formula <- "QUALITY ~ NARTIC + PCTGRT + PCTSUPP"
object <- lm(formula = formula, data = df)
BetaNB(formula = formula, data = df, B = B)
},
times = 10
)Summary of Benchmark Results
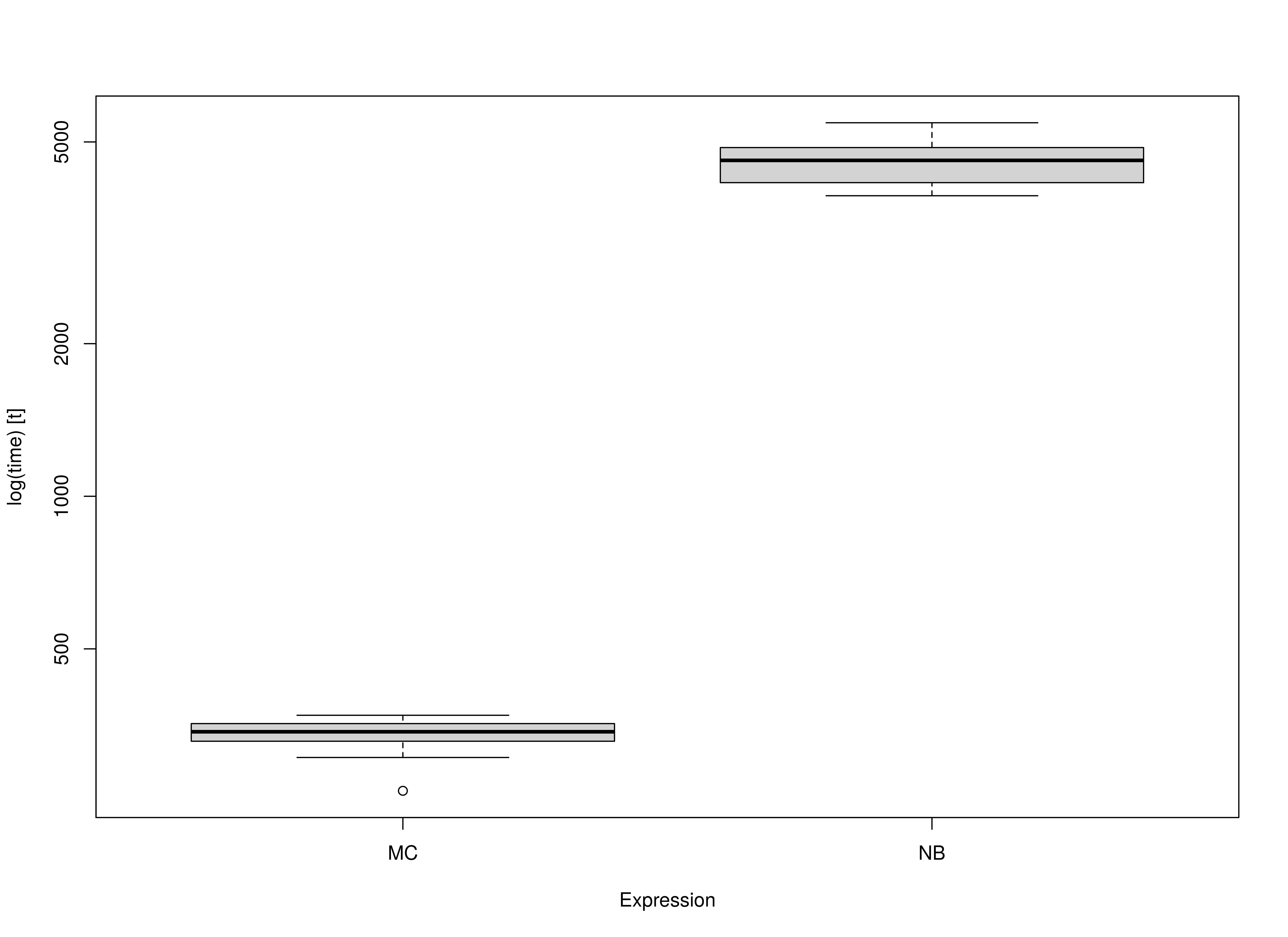
summary(benchmark, unit = "ms")
#> expr min lq mean median uq max neval
#> 1 MC 432.7853 448.3373 466.5032 459.4231 472.4815 534.8184 10
#> 2 NB 7162.7719 7215.6185 7245.5030 7233.9516 7260.3365 7427.5230 10Summary of Benchmark Results Relative to the Faster Method
summary(benchmark, unit = "relative")
#> expr min lq mean median uq max neval
#> 1 MC 1.00000 1.00000 1.00000 1.00000 1.00000 1.00000 10
#> 2 NB 16.55041 16.09417 15.53152 15.74573 15.36639 13.88793 10