Benchmark: Comparing the Monte Carlo Method with Nonparametric Bootstrapping (FIML)
Ivan Jacob Agaloos Pesigan
2025-10-19
Source:vignettes/benchmark-fiml.Rmd
benchmark-fiml.RmdWe compare the Monte Carlo (MC) method with nonparametric bootstrapping (NB) using the simple mediation model with missing data using full-information maximum likelihood. One advantage of MC over NB is speed. This is because the model is only fitted once in MC whereas it is fitted many times in NB.
Data
n <- 1000
a <- 0.50
b <- 0.50
cp <- 0.25
s2_em <- 1 - a^2
s2_ey <- 1 - cp^2 - a^2 * b^2 - b^2 * s2_em - 2 * cp * a * b
em <- rnorm(n = n, mean = 0, sd = sqrt(s2_em))
ey <- rnorm(n = n, mean = 0, sd = sqrt(s2_ey))
X <- rnorm(n = n)
M <- a * X + em
Y <- cp * X + b * M + ey
df <- data.frame(X, M, Y)
# Create data set with missing values.
miss <- sample(1:dim(df)[1], 300)
df[miss[1:100], "X"] <- NA
df[miss[101:200], "M"] <- NA
df[miss[201:300], "Y"] <- NAModel Specification
The indirect effect is defined by the product of the slopes of paths
X to M labeled as a and
M to Y labeled as b. In this
example, we are interested in the confidence intervals of
indirect defined as the product of a and
b using the := operator in the
lavaan model syntax.
model <- "
Y ~ cp * X + b * M
M ~ a * X
X ~~ X
indirect := a * b
direct := cp
total := cp + (a * b)
"Model Fitting
We can now fit the model using the sem() function from
lavaan. We are using missing = "fiml" to
handle missing data in lavaan.
fit <- sem(data = df, model = model)Monte Carlo Confidence Intervals
The fit lavaan object can then be passed to
the MC() function from semmcci to generate
Monte Carlo confidence intervals.
MC(fit, R = 100L, alpha = 0.05)
#> Monte Carlo Confidence Intervals
#> est se R 2.5% 97.5%
#> cp 0.2419 0.0332 100 0.1792 0.3070
#> b 0.5166 0.0308 100 0.4580 0.5785
#> a 0.4989 0.0319 100 0.4448 0.5615
#> X~~X 1.0951 0.0621 100 0.9856 1.2026
#> Y~~Y 0.5796 0.0307 100 0.5257 0.6413
#> M~~M 0.8045 0.0464 100 0.7325 0.9106
#> indirect 0.2577 0.0210 100 0.2234 0.3031
#> direct 0.2419 0.0332 100 0.1792 0.3070
#> total 0.4996 0.0322 100 0.4550 0.5681Nonparametric Bootstrap Confidence Intervals
Nonparametric bootstrap confidence intervals can be generated in
lavaan using the following.
parameterEstimates(
sem(
data = df,
model = model,
missing = "fiml",
se = "bootstrap",
bootstrap = 100L
)
)
#> lhs op rhs label est se z pvalue ci.lower ci.upper
#> 1 Y ~ X cp 0.234 0.030 7.721 0.000 0.169 0.287
#> 2 Y ~ M b 0.511 0.035 14.704 0.000 0.442 0.585
#> 3 M ~ X a 0.481 0.028 17.117 0.000 0.425 0.532
#> 4 X ~~ X 1.059 0.049 21.539 0.000 0.979 1.148
#> 5 Y ~~ Y 0.554 0.029 19.264 0.000 0.490 0.607
#> 6 M ~~ M 0.756 0.032 23.389 0.000 0.693 0.820
#> 7 Y ~1 -0.013 0.027 -0.473 0.636 -0.065 0.056
#> 8 M ~1 -0.022 0.030 -0.744 0.457 -0.077 0.044
#> 9 X ~1 0.002 0.036 0.069 0.945 -0.072 0.074
#> 10 indirect := a*b indirect 0.246 0.021 11.534 0.000 0.202 0.286
#> 11 direct := cp direct 0.234 0.030 7.721 0.000 0.169 0.287
#> 12 total := cp+(a*b) total 0.479 0.030 16.081 0.000 0.417 0.547Benchmark
Arguments
| Variables | Values | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| R | 1000 | Number of Monte Carlo replications. |
| B | 1000 | Number of bootstrap samples. |
benchmark_fiml_01 <- microbenchmark(
MC = {
fit <- sem(
data = df,
model = model,
missing = "fiml"
)
MC(
fit,
R = R,
decomposition = "chol",
pd = FALSE
)
},
NB = sem(
data = df,
model = model,
missing = "fiml",
se = "bootstrap",
bootstrap = B
),
times = 10
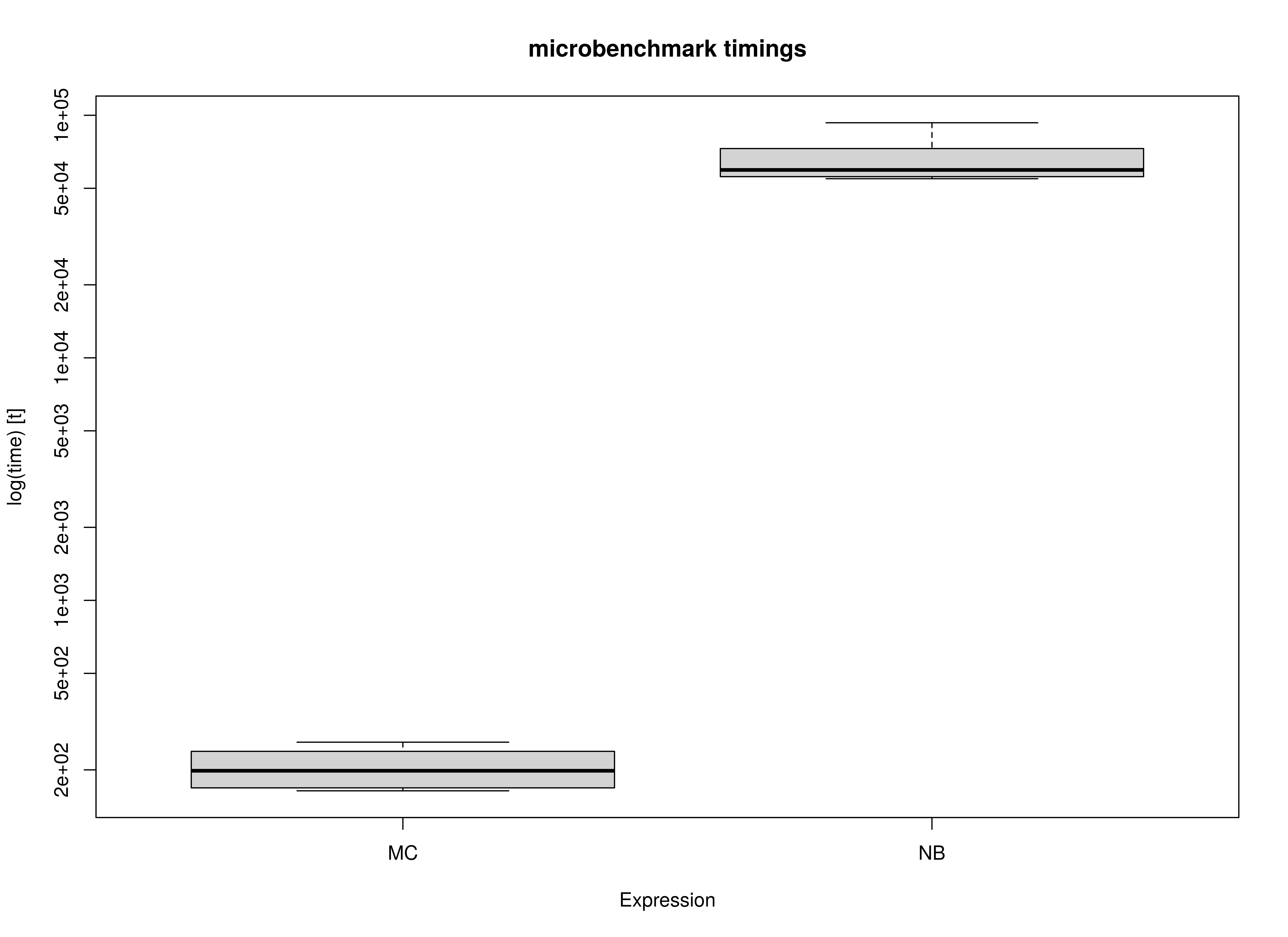
)Summary of Benchmark Results
summary(benchmark_fiml_01, unit = "ms")
#> expr min lq mean median uq max neval
#> 1 MC 121.7111 122.5368 124.5841 125.1569 125.8596 127.6093 10
#> 2 NB 27922.9926 27984.3329 28009.1665 27992.8715 28057.7444 28133.4957 10Summary of Benchmark Results Relative to the Faster Method
summary(benchmark_fiml_01, unit = "relative")
#> expr min lq mean median uq max neval
#> 1 MC 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 10
#> 2 NB 229.4202 228.3749 224.8214 223.6622 222.9289 220.4658 10Benchmark - Monte Carlo Method with Precalculated Estimates
fit <- sem(
data = df,
model = model,
missing = "fiml"
)
benchmark_fiml_02 <- microbenchmark(
MC = MC(
fit,
R = R,
decomposition = "chol",
pd = FALSE
),
NB = sem(
data = df,
model = model,
missing = "fiml",
se = "bootstrap",
bootstrap = B
),
times = 10
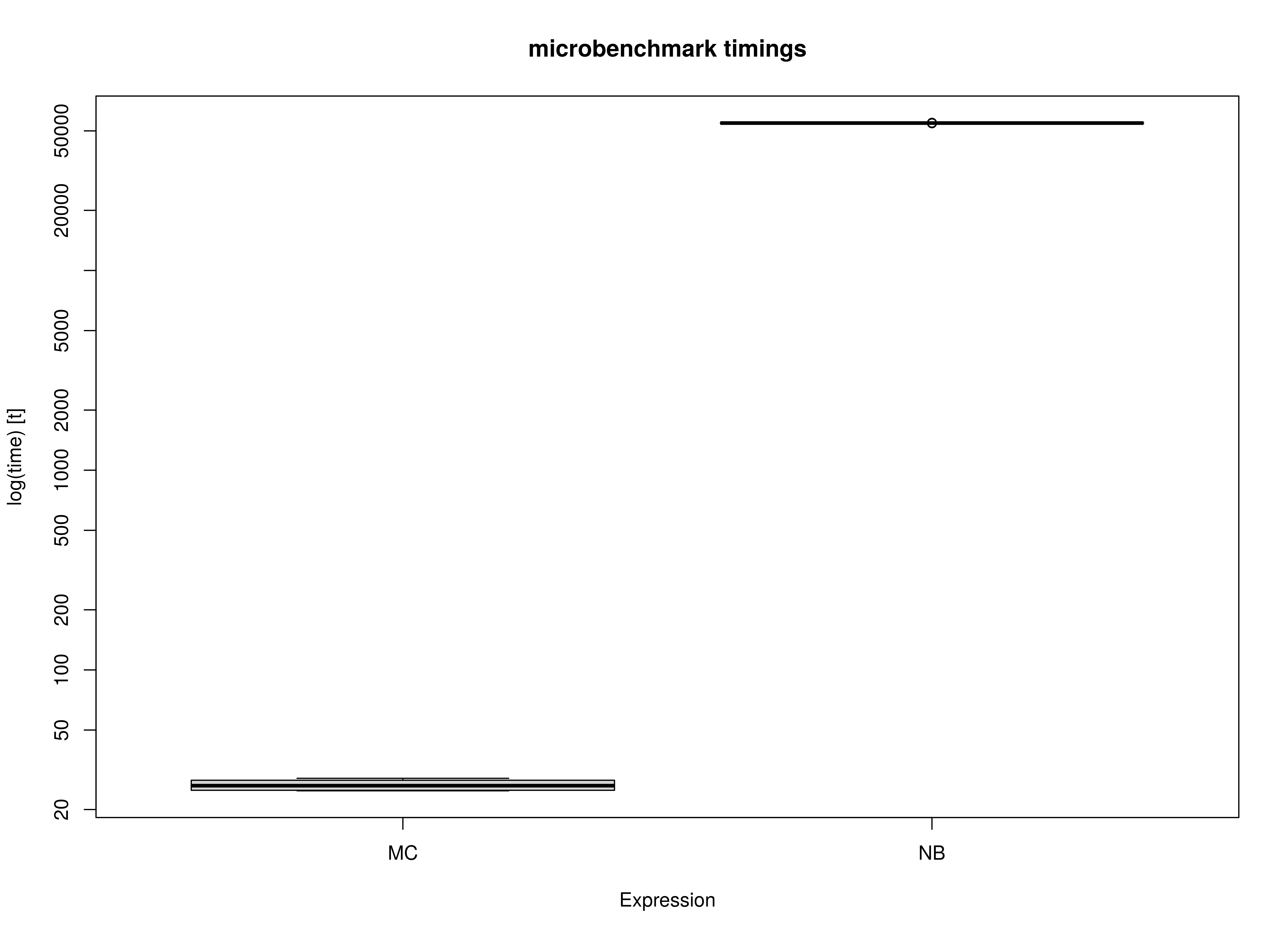
)Summary of Benchmark Results
summary(benchmark_fiml_02, unit = "ms")
#> expr min lq mean median uq max
#> 1 MC 21.87685 22.12413 24.21625 23.49522 26.27235 27.63496
#> 2 NB 27614.25595 27851.34753 27899.64184 27950.19922 28000.03878 28058.31435
#> neval
#> 1 10
#> 2 10Summary of Benchmark Results Relative to the Faster Method
summary(benchmark_fiml_02, unit = "relative")
#> expr min lq mean median uq max neval
#> 1 MC 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.00 10
#> 2 NB 1262.259 1258.867 1152.104 1189.612 1065.761 1015.32 10