Total, Direct, and Indirect Effects in Continuous-Time Mediation Model (Bootstrap)
Ivan Jacob Agaloos Pesigan
2026-02-04
Source:vignettes/med-boot.Rmd
med-boot.RmdThe cTMed package provides a bootstrap approach, in
addition to the delta and Monte Carlo methods, for estimating and
quantifying uncertainty in total, direct, and indirect effects within
continuous-time mediation models across different time intervals.
In this example, we will use the fitted model from Fit
the Continuous-Time Vector Autoregressive Model Using the dynr
Package. The object fit represents a fitted CT-VAR
model created using the dynr package.
summary(fit)
#> Coefficients:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value ci.lower ci.upper Pr(>|t|)
#> phi_1_1 -0.351839 0.036416 -9.662 -0.423213 -0.280465 <2e-16 ***
#> phi_2_1 0.744282 0.021777 34.177 0.701599 0.786964 <2e-16 ***
#> phi_3_1 -0.458680 0.023534 -19.490 -0.504806 -0.412554 <2e-16 ***
#> phi_1_2 0.017311 0.031705 0.546 -0.044829 0.079451 0.2925
#> phi_2_2 -0.488821 0.019277 -25.358 -0.526602 -0.451039 <2e-16 ***
#> phi_3_2 0.726800 0.020871 34.824 0.685894 0.767706 <2e-16 ***
#> phi_1_3 -0.023814 0.024025 -0.991 -0.070903 0.023275 0.1608
#> phi_2_3 -0.009810 0.014718 -0.667 -0.038657 0.019036 0.2525
#> phi_3_3 -0.688334 0.016040 -42.913 -0.719773 -0.656896 <2e-16 ***
#> sigma_1_1 0.242180 0.006794 35.646 0.228864 0.255496 <2e-16 ***
#> sigma_2_1 0.023273 0.002545 9.146 0.018285 0.028261 <2e-16 ***
#> sigma_3_1 -0.050574 0.002749 -18.395 -0.055963 -0.045186 <2e-16 ***
#> sigma_2_2 0.070722 0.001907 37.093 0.066985 0.074458 <2e-16 ***
#> sigma_3_2 0.014987 0.001381 10.854 0.012281 0.017694 <2e-16 ***
#> sigma_3_3 0.072376 0.002099 34.475 0.068261 0.076491 <2e-16 ***
#> theta_1_1 0.198861 0.001170 169.909 0.196567 0.201155 <2e-16 ***
#> theta_2_2 0.199520 0.001000 199.500 0.197560 0.201480 <2e-16 ***
#> theta_3_3 0.201172 0.001016 198.052 0.199181 0.203162 <2e-16 ***
#> mu0_1_1 0.006324 0.111110 0.057 -0.211447 0.224095 0.4773
#> mu0_2_1 -0.042530 0.114320 -0.372 -0.266593 0.181533 0.3549
#> mu0_3_1 0.130043 0.102109 1.274 -0.070086 0.330172 0.1014
#> sigma0_1_1 1.150287 0.168811 6.814 0.819425 1.481150 <2e-16 ***
#> sigma0_2_1 0.413648 0.133495 3.099 0.152003 0.675293 0.0010 ***
#> sigma0_3_1 0.225993 0.123478 1.830 -0.016019 0.468006 0.0336 *
#> sigma0_2_2 1.221957 0.182233 6.705 0.864787 1.579128 <2e-16 ***
#> sigma0_3_2 0.235327 0.117629 2.001 0.004779 0.465875 0.0227 *
#> sigma0_3_3 0.962594 0.142152 6.772 0.683981 1.241207 <2e-16 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> -2 log-likelihood value at convergence = 429365.49
#> AIC = 429419.49
#> BIC = 429676.34We need to extract the estimated parameters from the fitted object, which will be used to generate bootstrap samples.
est <- coef(fit)
n
#> [1] 100
time
#> [1] 1000
delta_t
#> [1] 0.1
lambda
#> [,1] [,2] [,3]
#> [1,] 1 0 0
#> [2,] 0 1 0
#> [3,] 0 0 1
nu
#> [1] 0 0 0
mu
#> [1] 0 0 0
mu0 <- est[
c(
"mu0_1_1",
"mu0_2_1",
"mu0_3_1"
)
]
mu0
#> mu0_1_1 mu0_2_1 mu0_3_1
#> 0.006324029 -0.042529883 0.130043337
sigma0 <- matrix(
data = est[
c(
"sigma0_1_1",
"sigma0_2_1",
"sigma0_3_1",
"sigma0_2_1",
"sigma0_2_2",
"sigma0_3_2",
"sigma0_3_1",
"sigma0_3_2",
"sigma0_3_3"
)
],
nrow = 3,
ncol = 3
)
sigma0
#> [,1] [,2] [,3]
#> [1,] 1.1502873 0.4136480 0.2259932
#> [2,] 0.4136480 1.2219574 0.2353267
#> [3,] 0.2259932 0.2353267 0.9625940
sigma0_l <- t(chol(sigma0))
phi <- matrix(
data = est[
c(
"phi_1_1",
"phi_2_1",
"phi_3_1",
"phi_1_2",
"phi_2_2",
"phi_3_2",
"phi_1_3",
"phi_2_3",
"phi_3_3"
)
],
nrow = 3,
ncol = 3
)
phi
#> [,1] [,2] [,3]
#> [1,] -0.3518392 0.01731083 -0.023814339
#> [2,] 0.7442816 -0.48882067 -0.009810166
#> [3,] -0.4586796 0.72679980 -0.688334177
sigma <- matrix(
data = est[
c(
"sigma_1_1", "sigma_2_1", "sigma_3_1",
"sigma_2_1", "sigma_2_2", "sigma_3_2",
"sigma_3_1", "sigma_3_2", "sigma_3_3"
)
],
nrow = 3,
ncol = 3
)
sigma
#> [,1] [,2] [,3]
#> [1,] 0.24218026 0.02327296 -0.05057416
#> [2,] 0.02327296 0.07072156 0.01498732
#> [3,] -0.05057416 0.01498732 0.07237598
sigma_l <- t(chol(sigma))
theta <- diag(3)
diag(theta) <- est[
c(
"theta_1_1",
"theta_2_2",
"theta_3_3"
)
]
theta
#> [,1] [,2] [,3]
#> [1,] 0.1988611 0.0000000 0.0000000
#> [2,] 0.0000000 0.1995203 0.0000000
#> [3,] 0.0000000 0.0000000 0.2011716
theta_l <- t(chol(theta))
R <- 1000L # use at least 1000 in actual research
path <- getwd()
prefix <- "ou"The estimated parameters are then passed as arguments to the
PBSSMOUFixed function from the bootStateSpace
package, which generates a parametric bootstrap sampling distribution of
the parameter estimates. The argument R specifies the
number of bootstrap replications. The generated data and model estimates
are stored in path using the specified prefix
for the file names. The ncores = parallel::detectCores()
argument instructs the function to use all available CPU cores in the
system.
NOTE: Fitting the CT-VAR model multiple times is computationally intensive.
library(bootStateSpace)
boot <- PBSSMOUFixed(
R = R,
path = path,
prefix = prefix,
n = n,
time = time,
delta_t = delta_t,
mu0 = mu0,
sigma0_l = sigma0_l,
mu = mu,
phi = phi,
sigma_l = sigma_l,
nu = nu,
lambda = lambda,
theta_l = theta_l,
ncores = parallel::detectCores(),
seed = 42,
clean = FALSE
)The extract function from the
bootStateSpace package is used to extract the bootstrap phi
matrices as well as the sigma matrices.
phi <- extract(object = boot, what = "phi")
sigma <- extract(object = boot, what = "sigma")In this example, we aim to calculate the total, direct, and indirect
effects of x on y, mediated through
m, over time intervals ranging from 0 to 10.
# time intervals
delta_t <- seq(from = 0, to = 10, length.out = 1000)We also need the estimated drift matrix from the original sample.
# estimated drift matrix
phi_hat <- matrix(
data = est[
c(
"phi_1_1",
"phi_2_1",
"phi_3_1",
"phi_1_2",
"phi_2_2",
"phi_3_2",
"phi_1_3",
"phi_2_3",
"phi_3_3"
)
],
nrow = 3,
ncol = 3
)
colnames(phi_hat) <- rownames(phi_hat) <- c("x", "m", "y")For the standardized effects, the estimated process noise covariance matrix from the original sample is also needed.
# estimated process noise covariance matrix
sigma_hat <- matrix(
data = est[
c(
"sigma_1_1", "sigma_2_1", "sigma_3_1",
"sigma_2_1", "sigma_2_2", "sigma_3_2",
"sigma_3_1", "sigma_3_2", "sigma_3_3"
)
],
nrow = 3,
ncol = 3
)Bootstrap Method
library(cTMed)
boot <- BootMed(
phi = phi,
phi_hat = phi_hat,
delta_t = delta_t,
from = "x",
to = "y",
med = "m",
ncores = parallel::detectCores() # use multiple cores
)
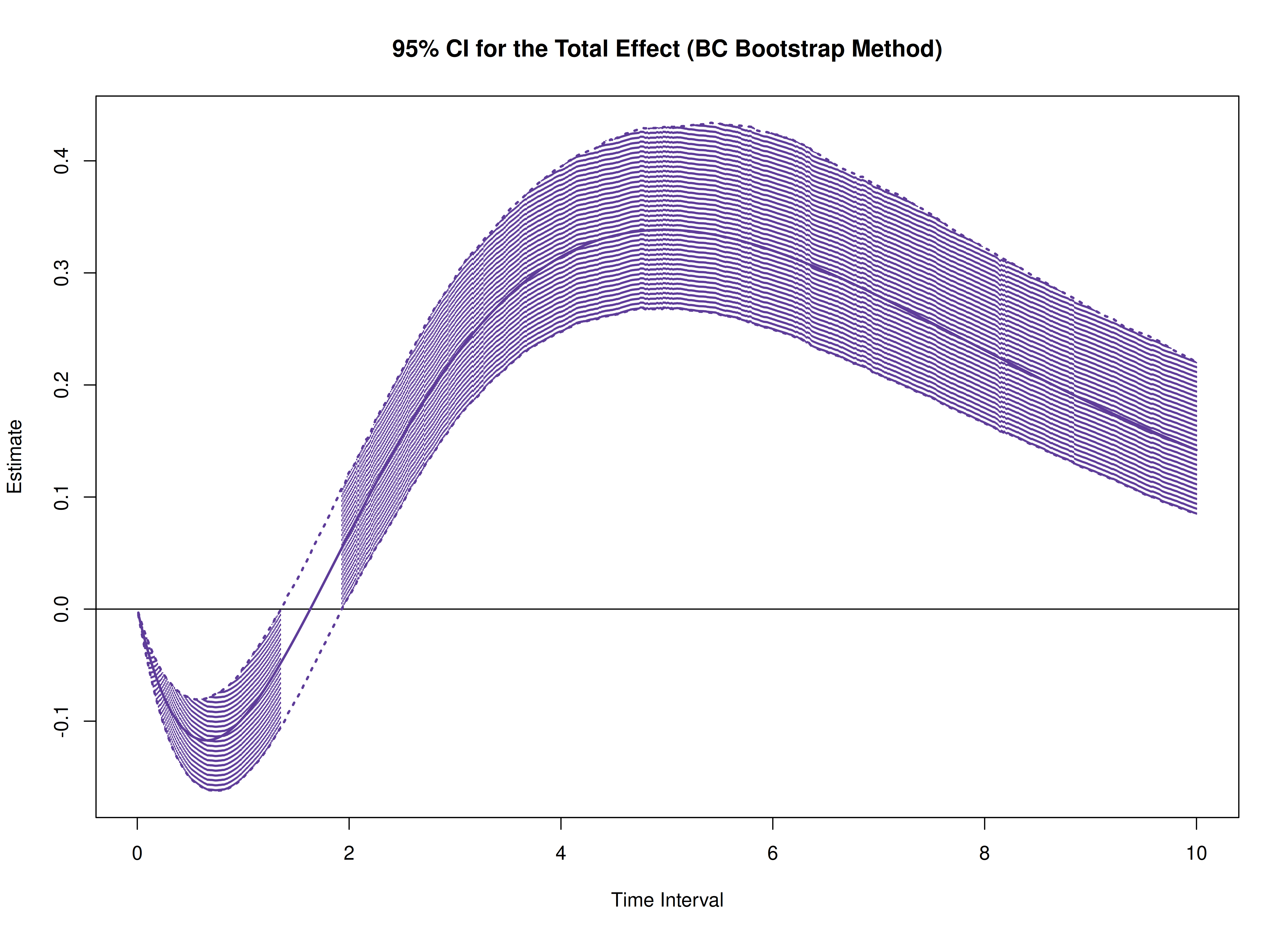
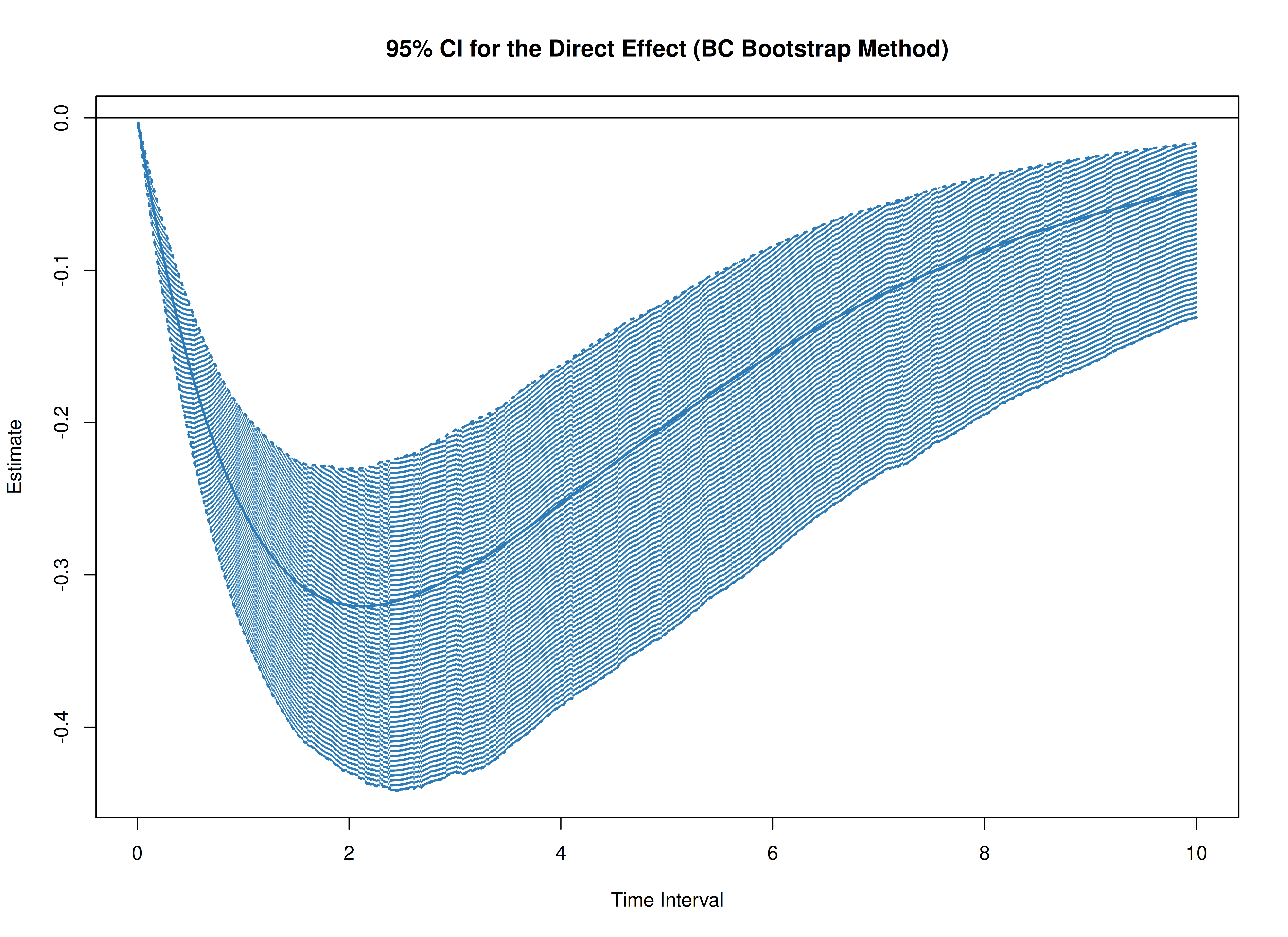
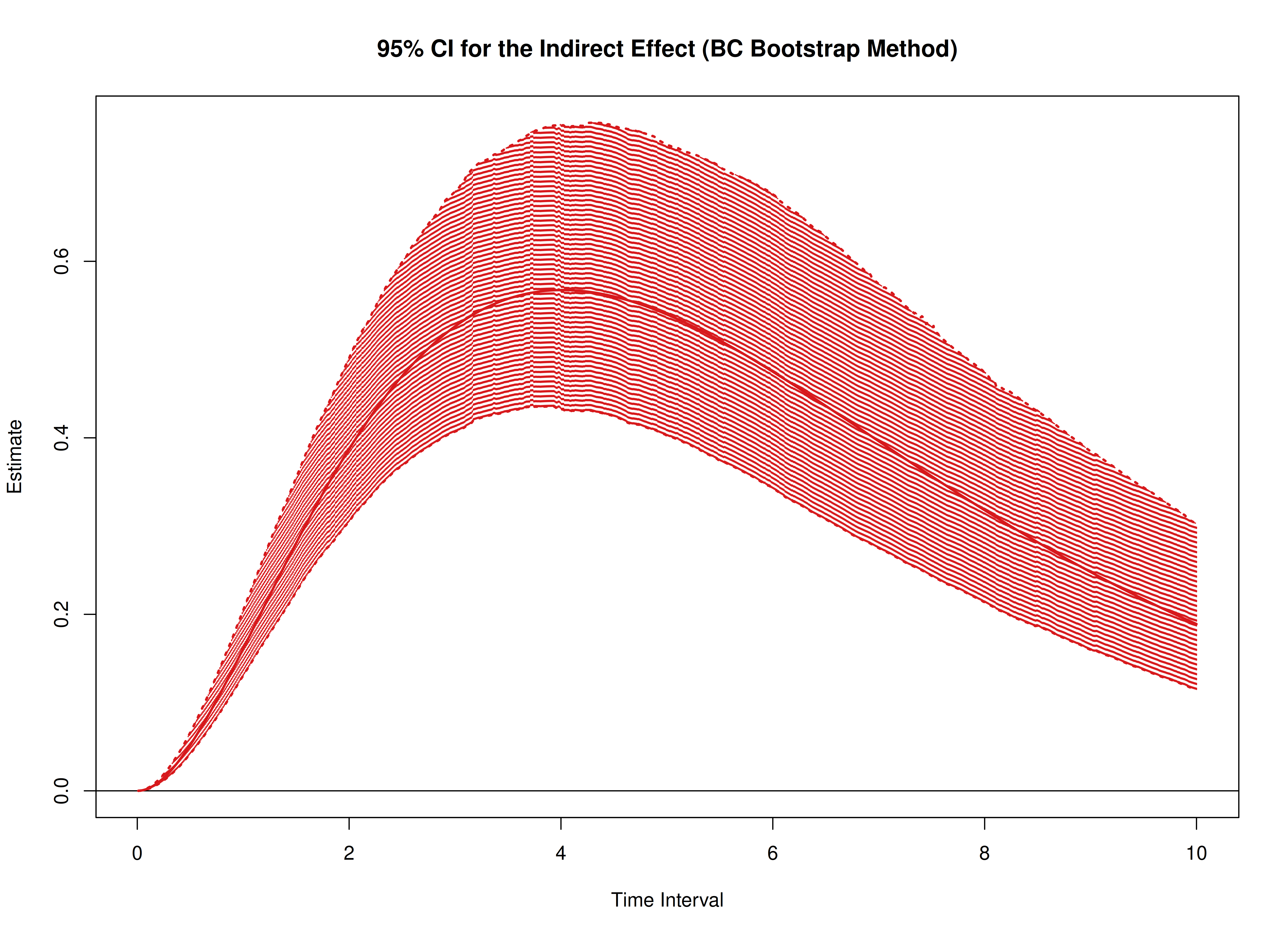
plot(boot)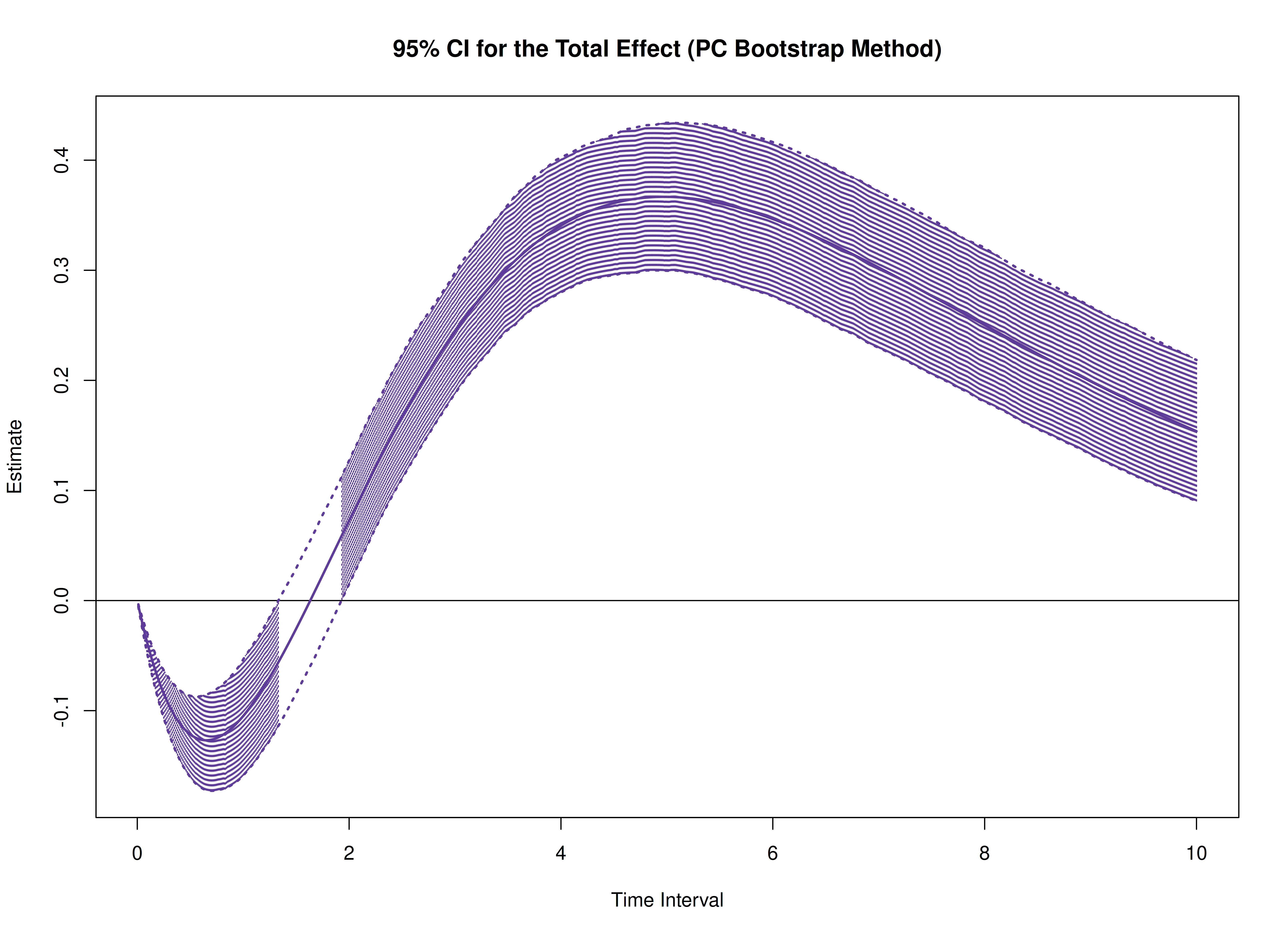
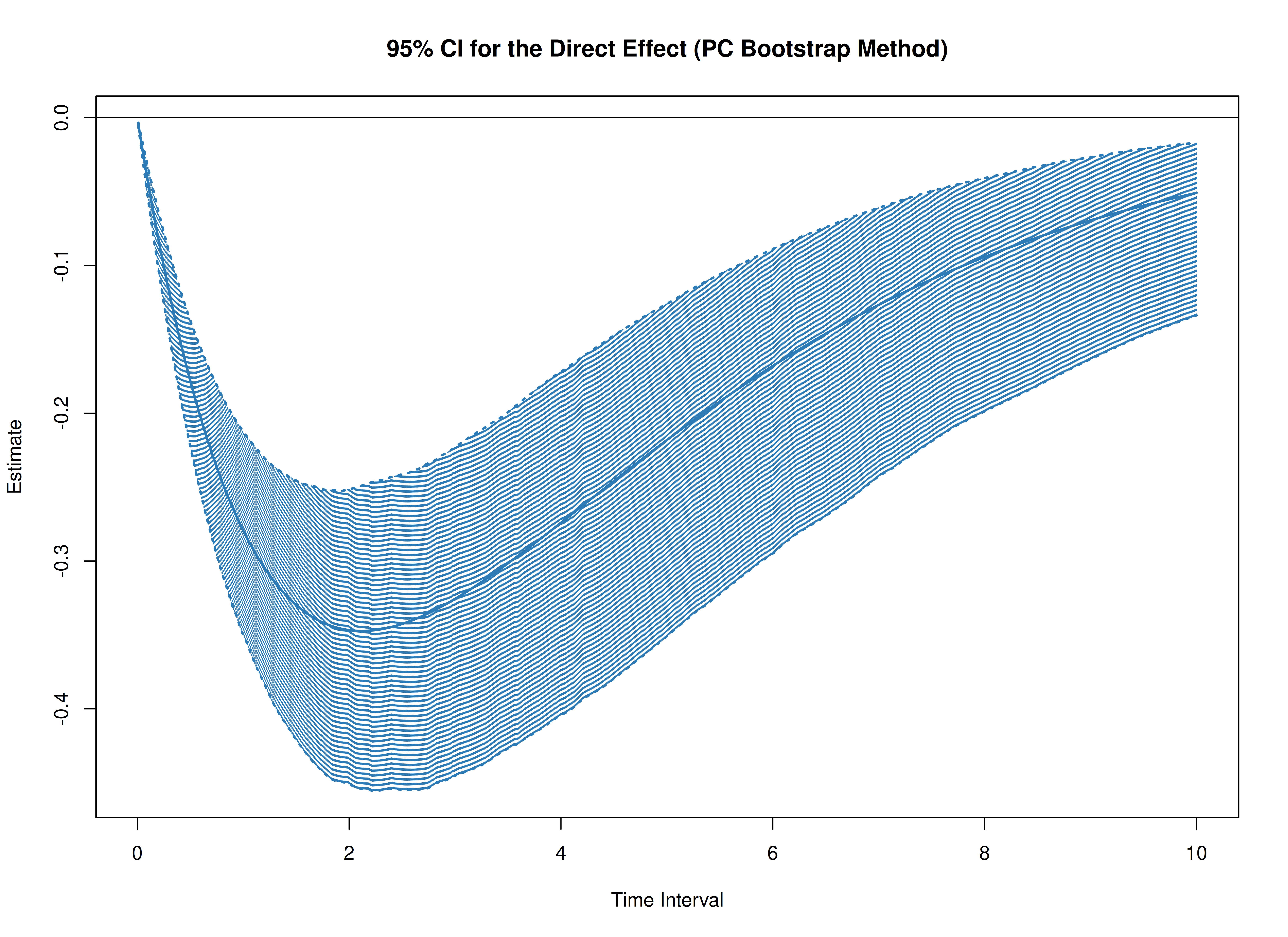
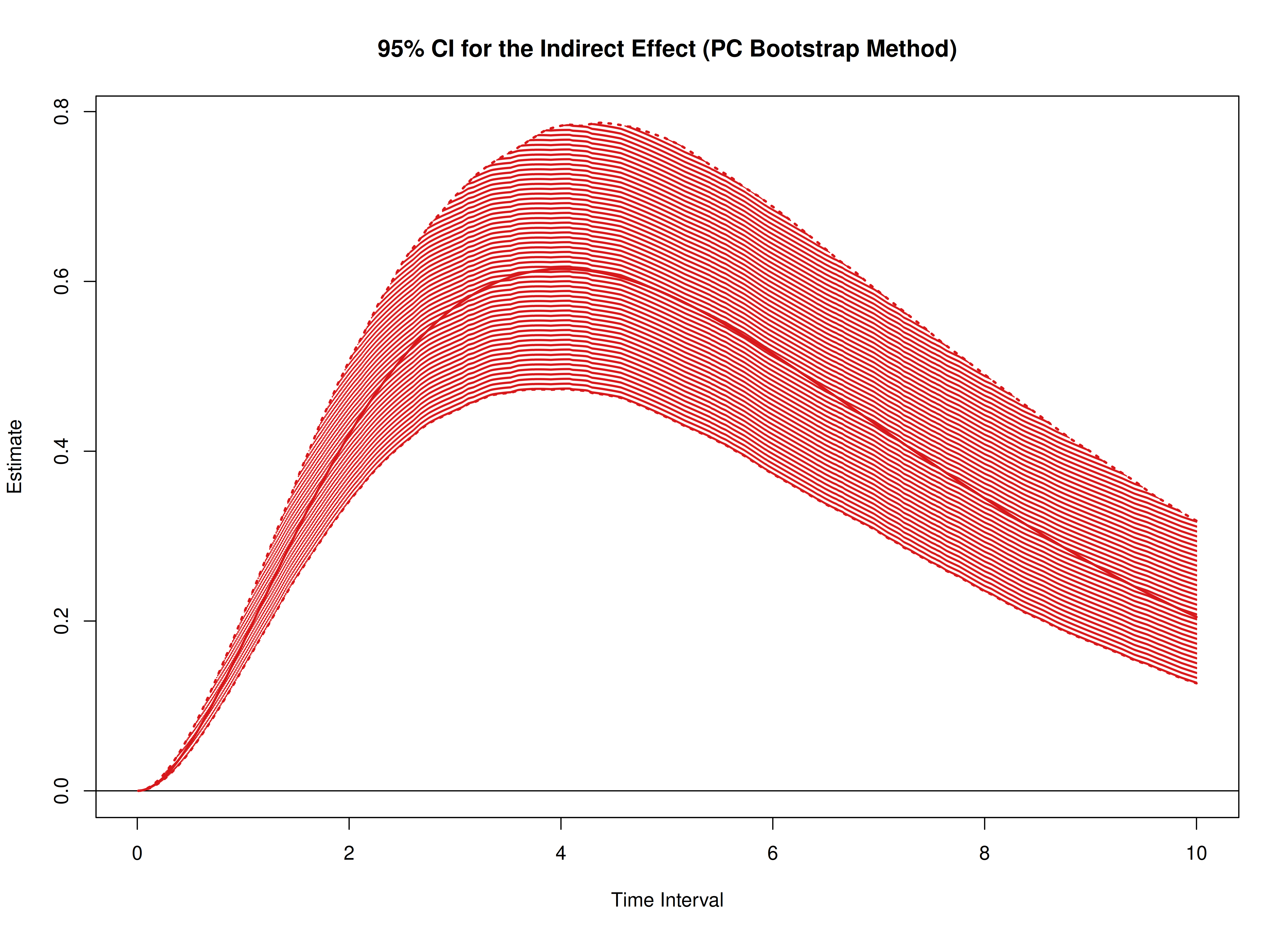
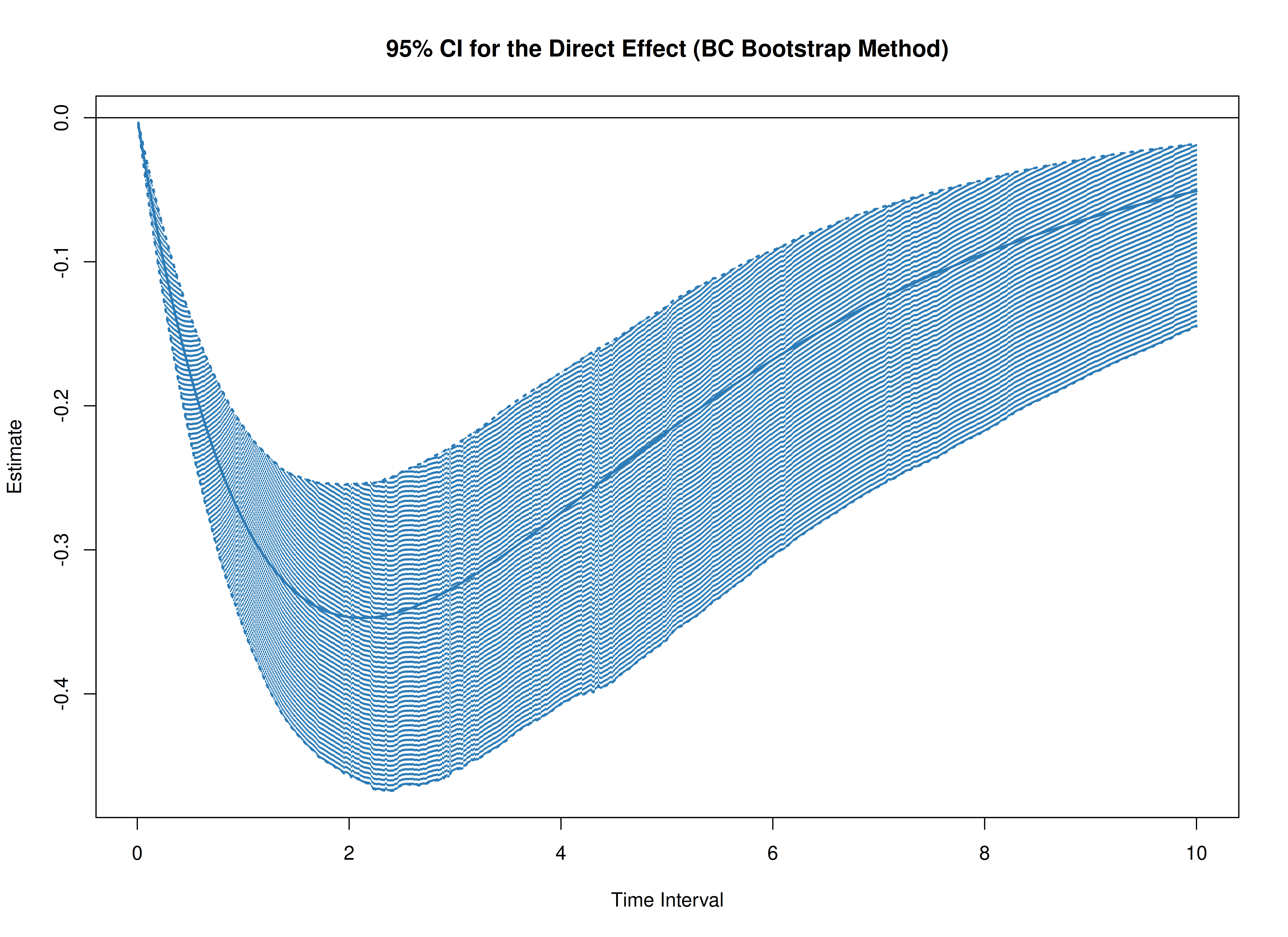
plot(boot, type = "bc")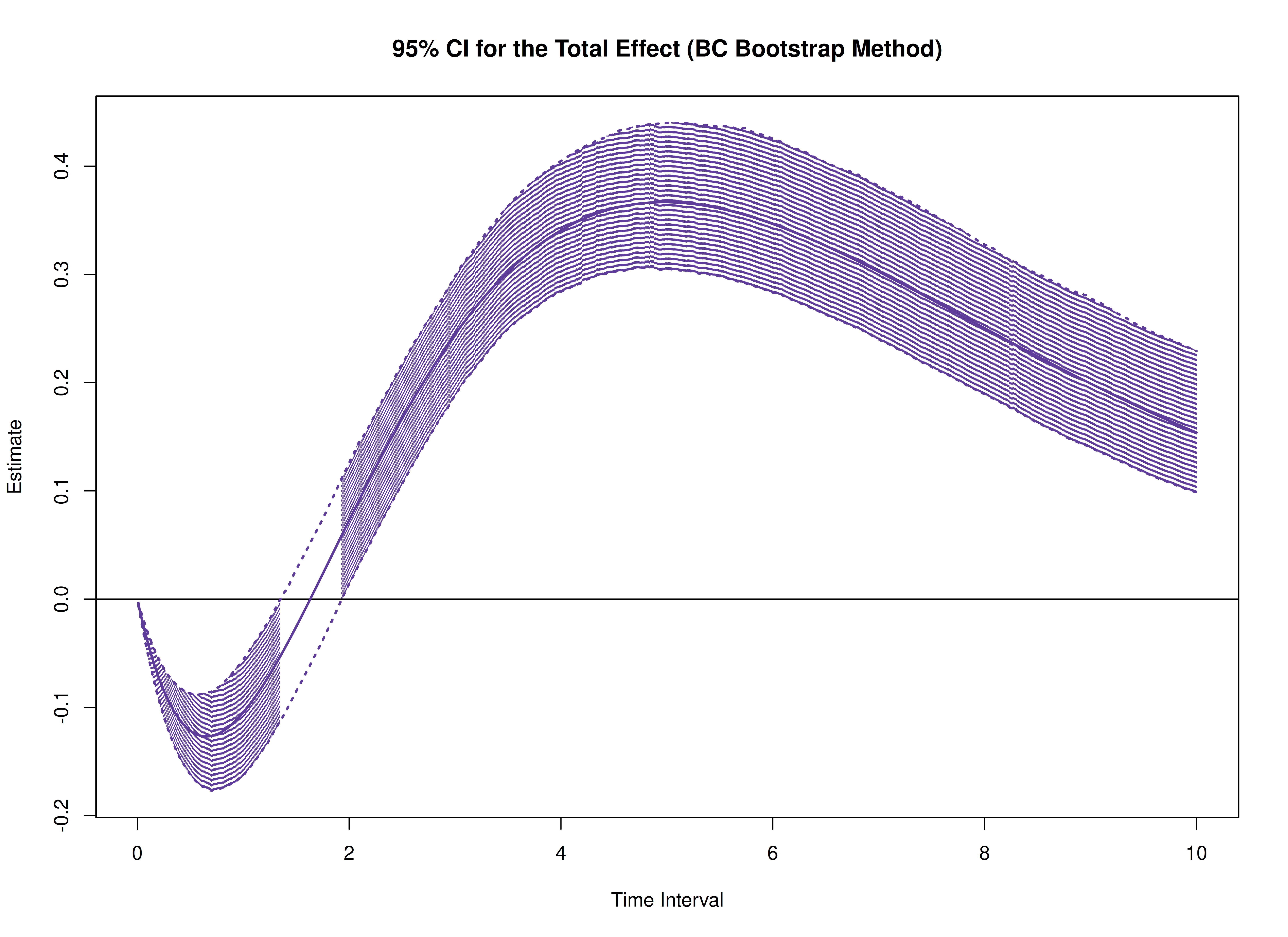
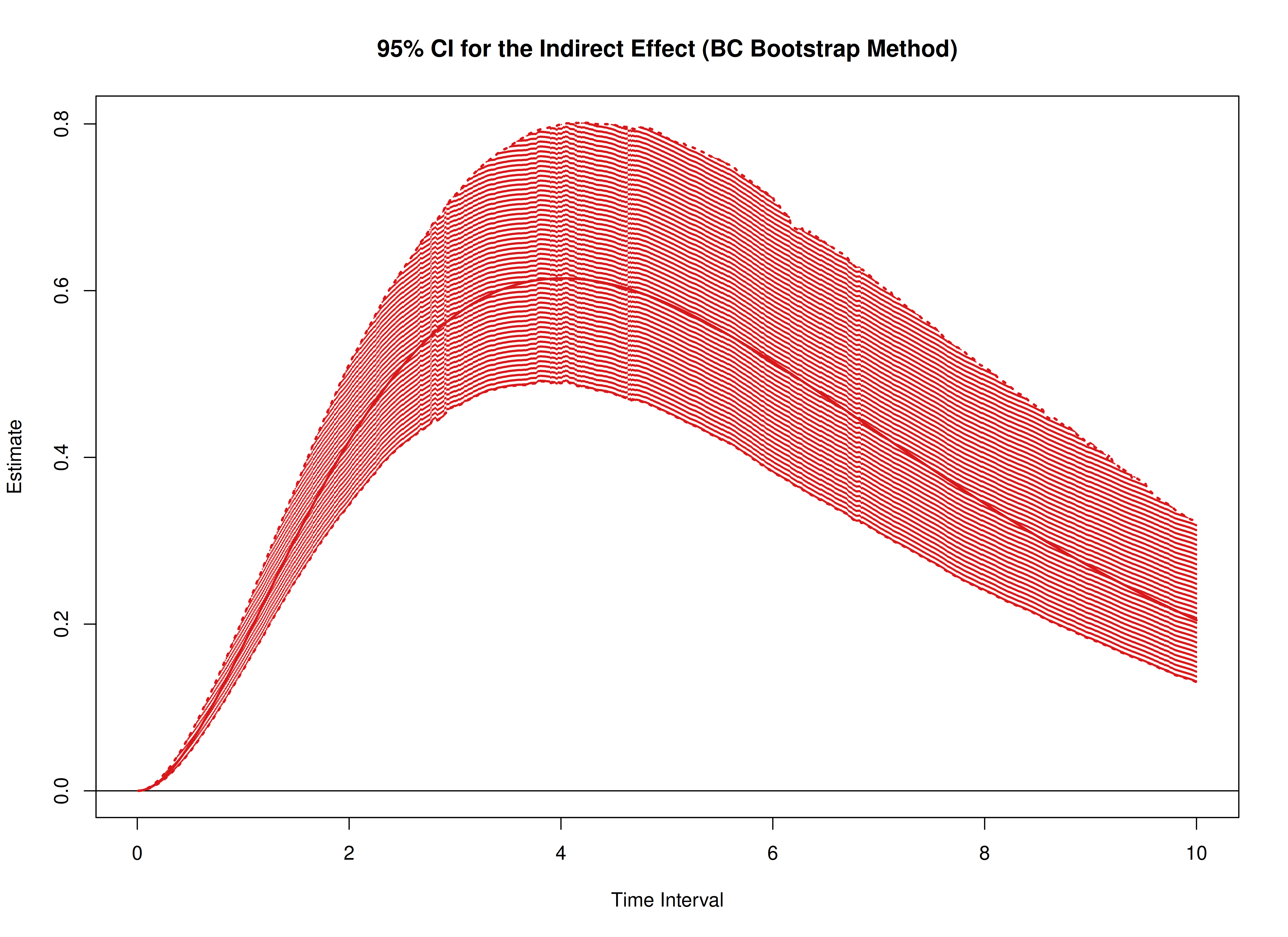
The following generates bootstrap confidence intervals for the standardized effects.
boot <- BootMedStd(
phi = phi,
sigma = sigma,
phi_hat = phi_hat,
sigma_hat = sigma_hat,
delta_t = delta_t,
from = "x",
to = "y",
med = "m",
ncores = parallel::detectCores() # use multiple cores
)
plot(boot)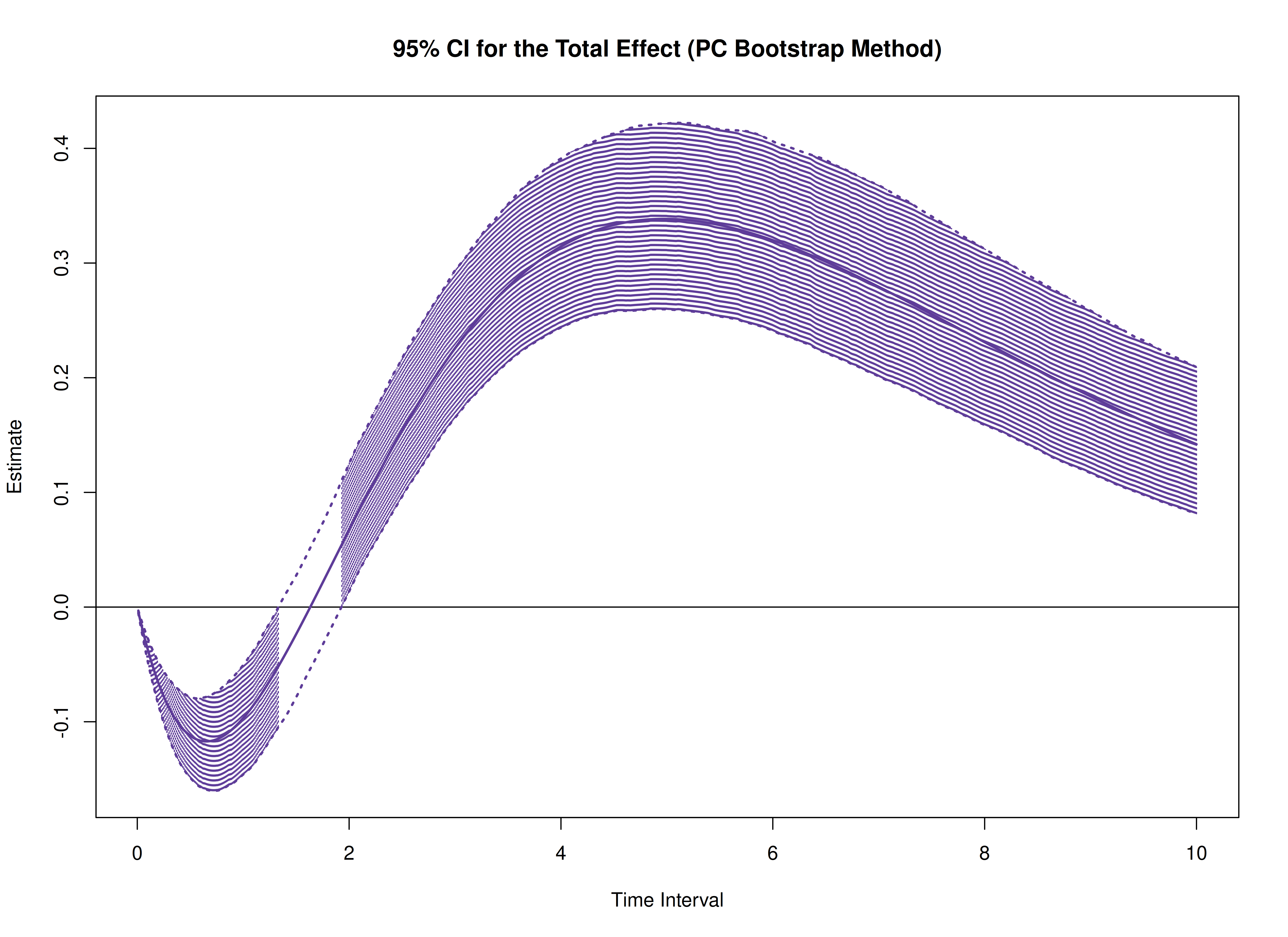
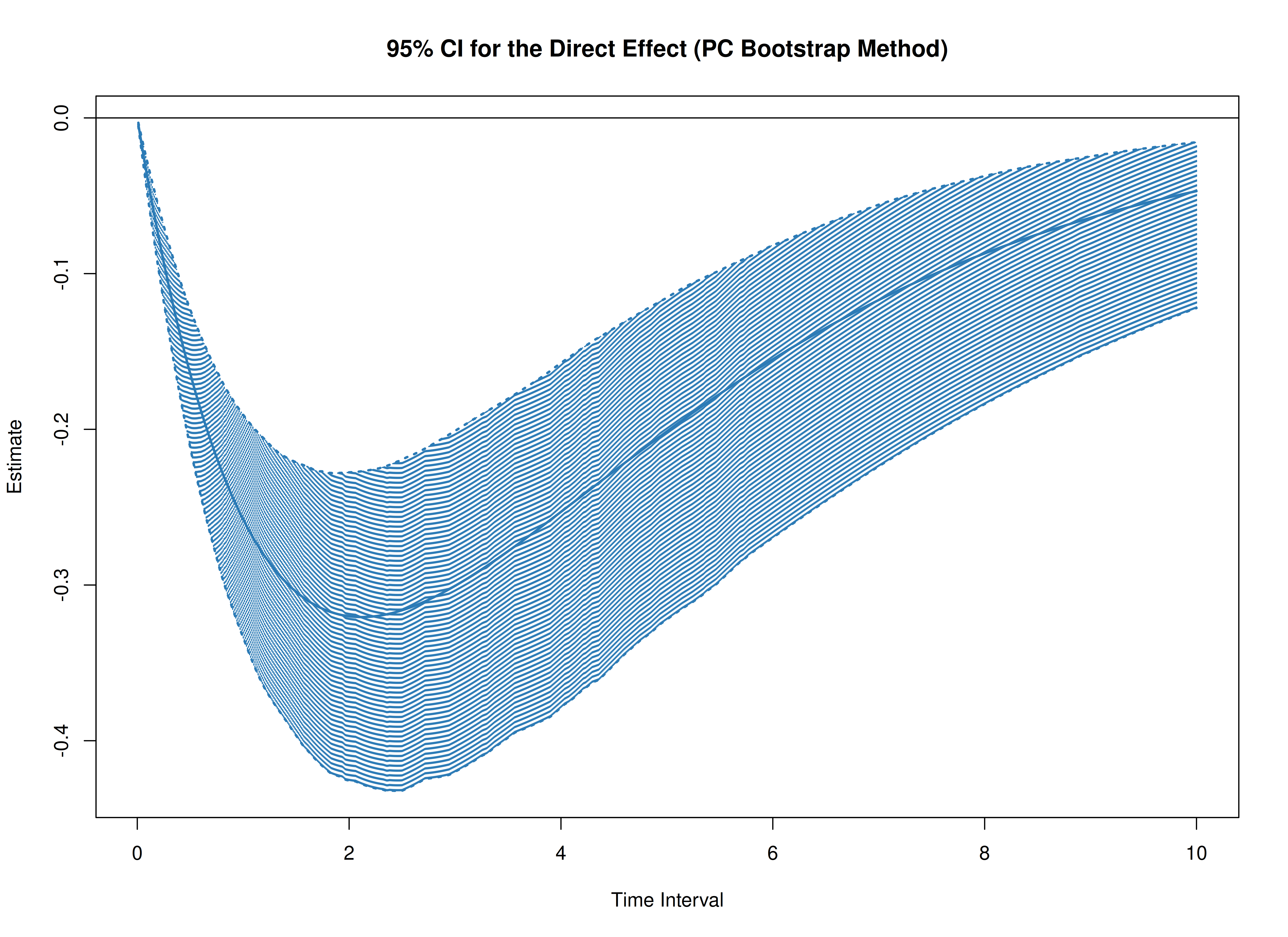

plot(boot, type = "bc")